1ACJ Protein Structure Exploration with Molecular World
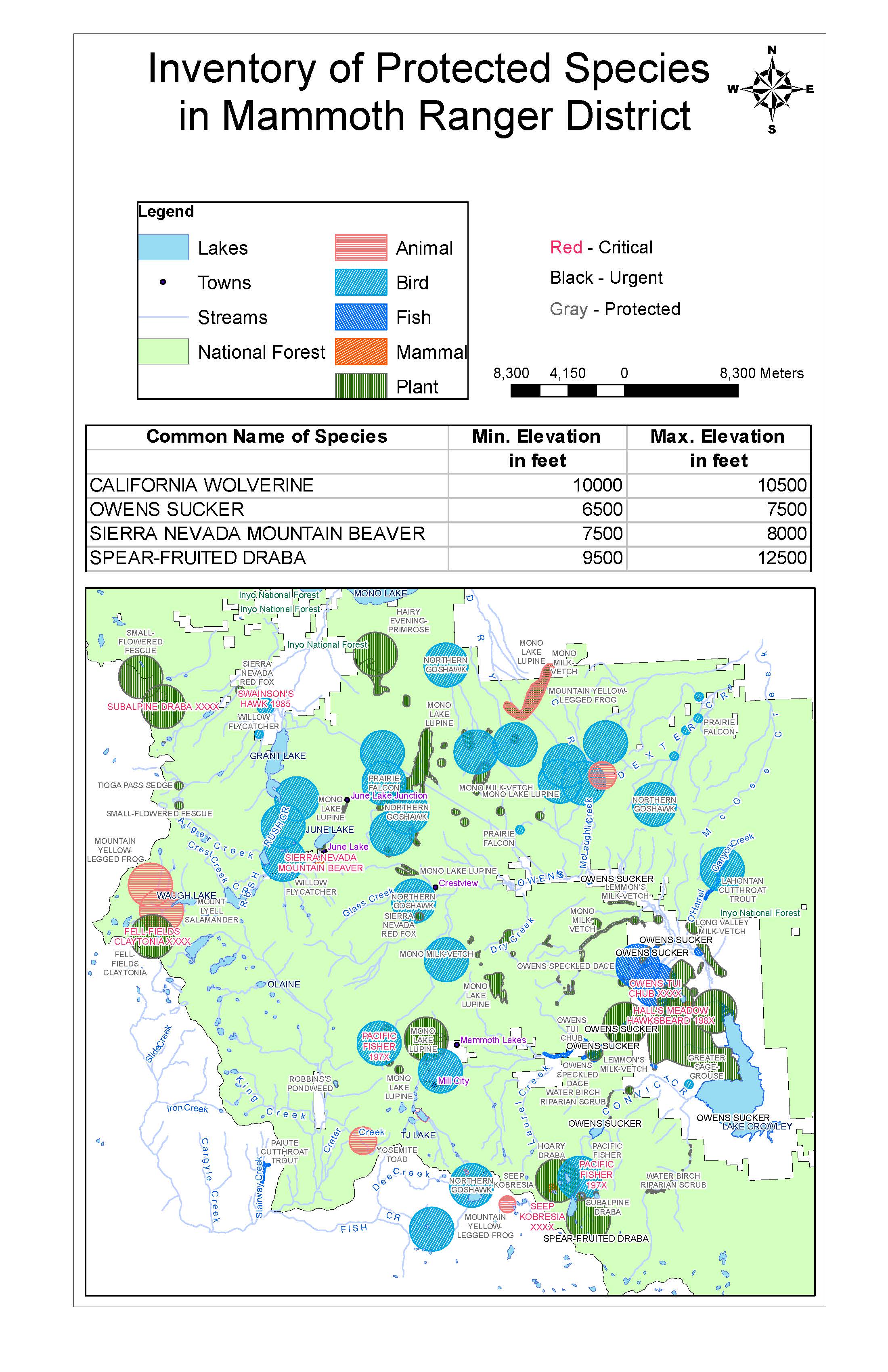
1ACJ – Acetylcholinesterase
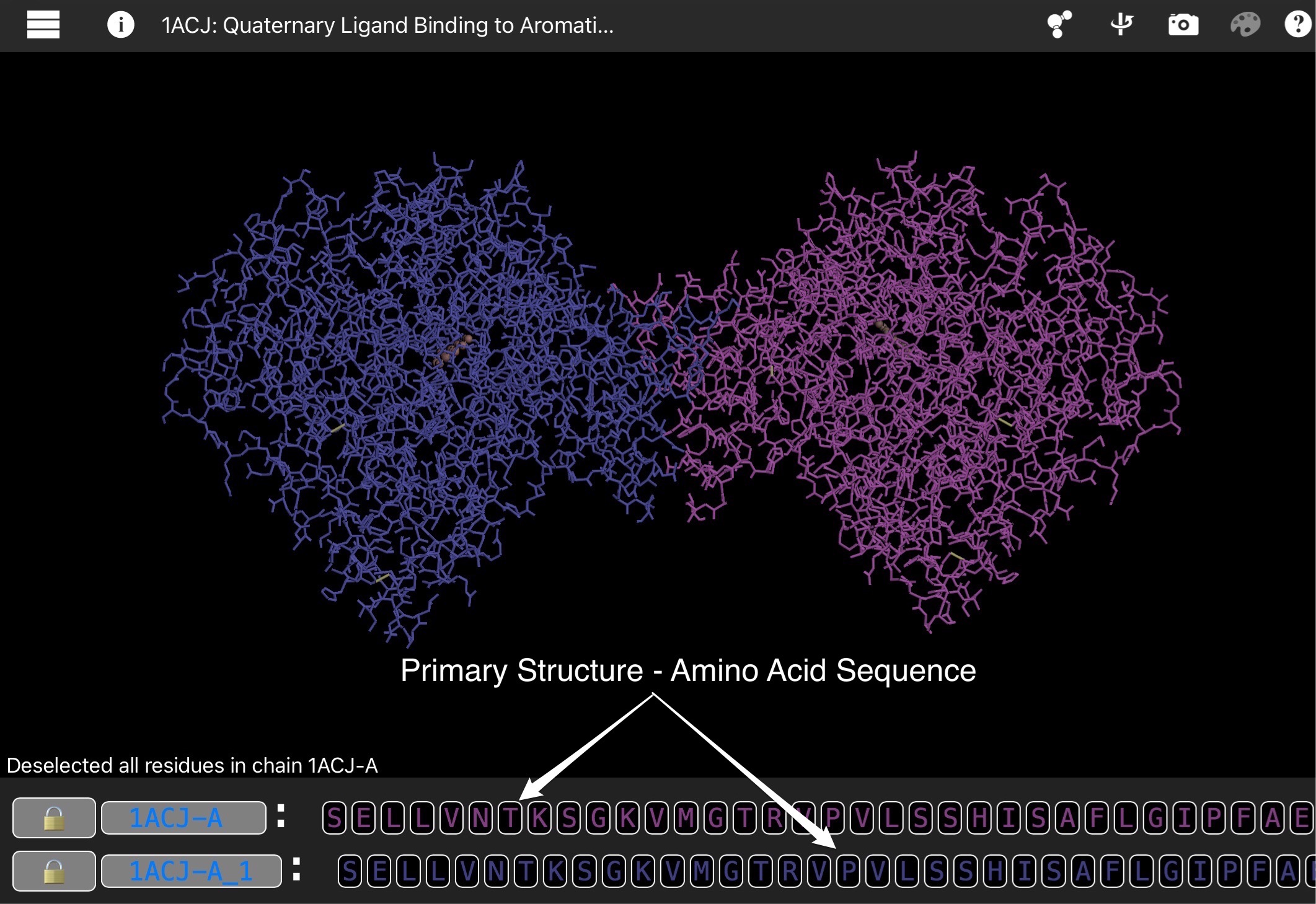
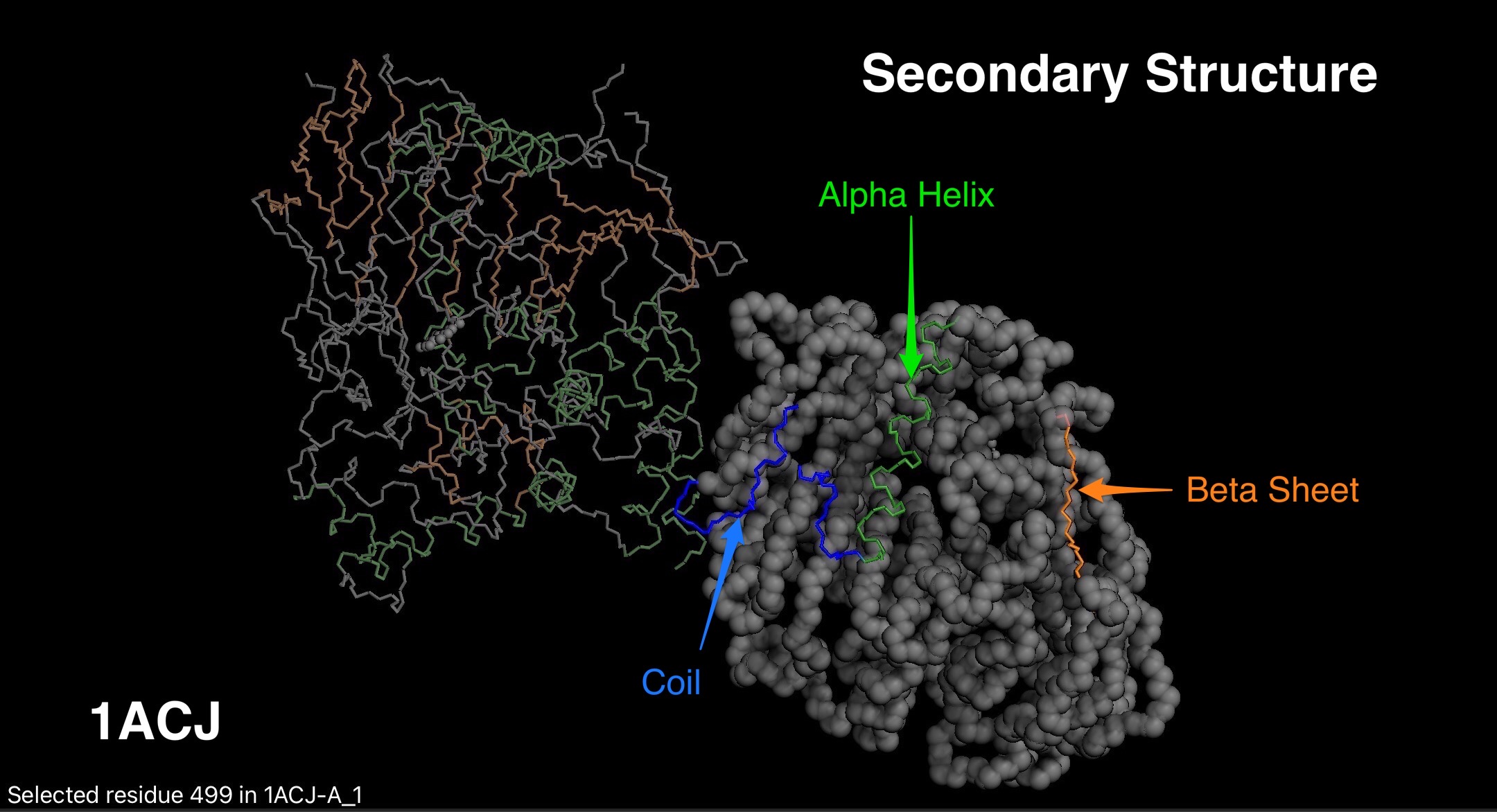
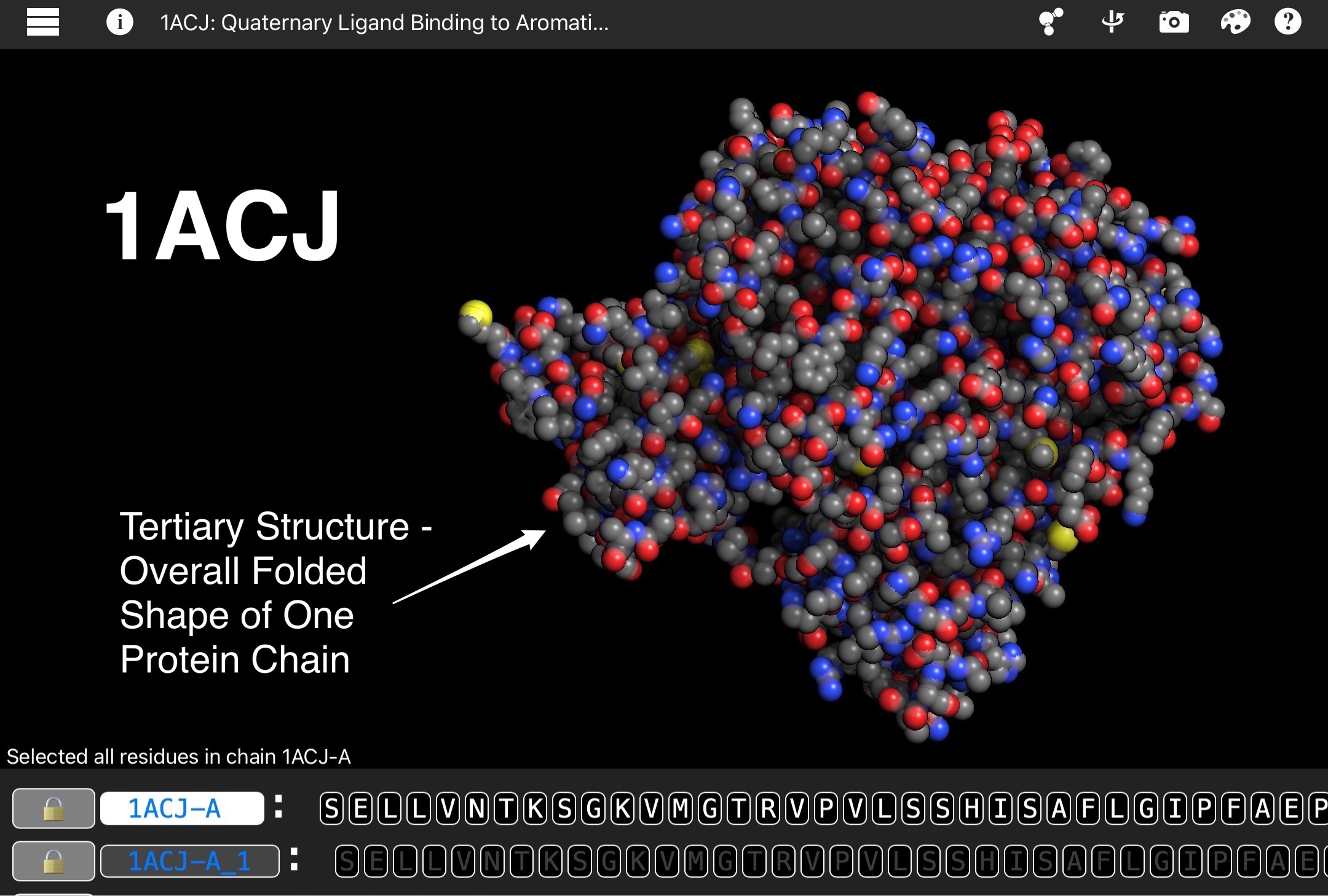
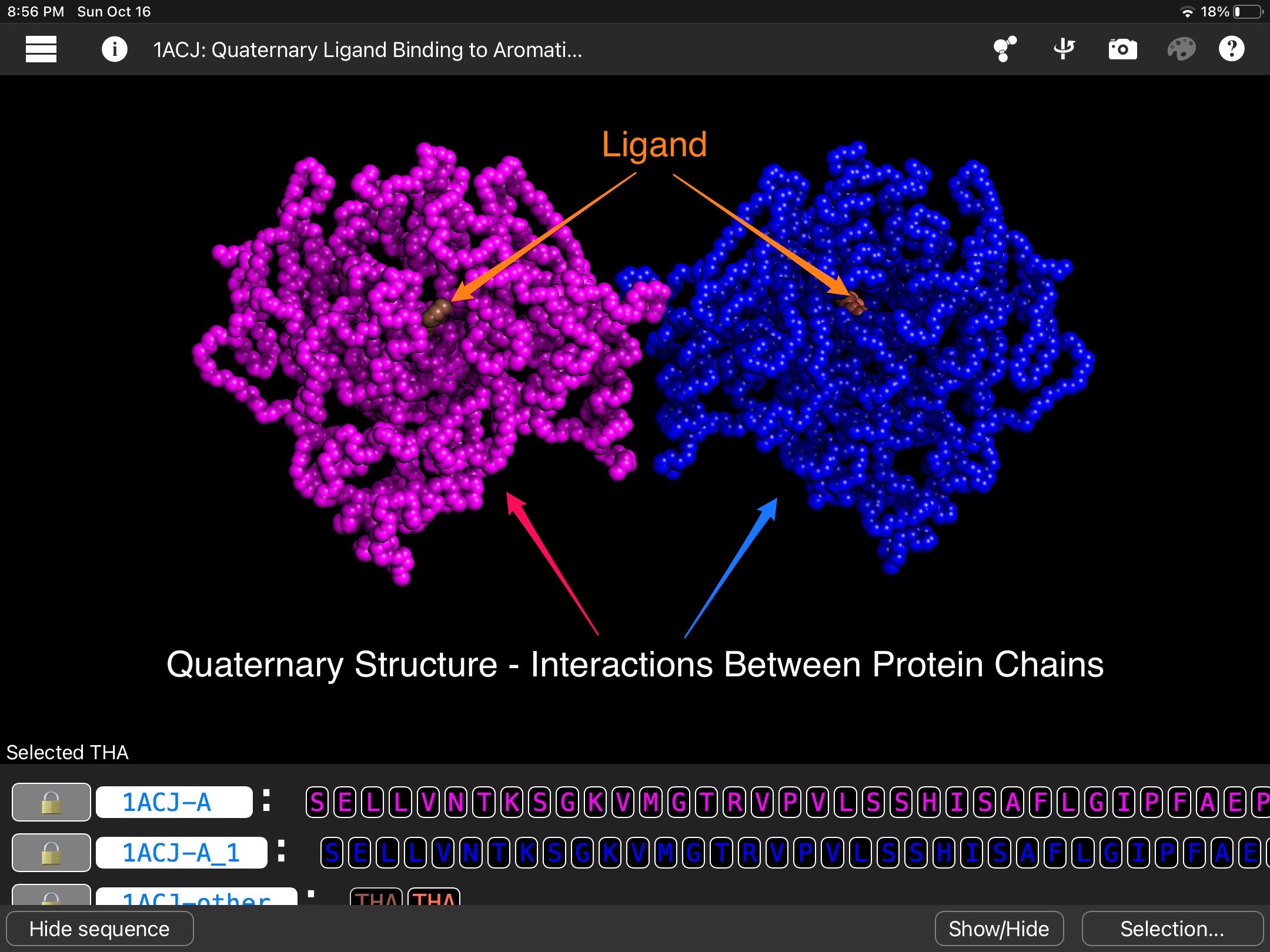
Acetylcholinesterase is an enzyme that digests acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that carries signals from nerve cells to muscle cells. Once a message is delivered, acetylcholinesterase recycles acetylcholine into acetic acid and choline at a rate of about 80 microseconds per molecule. Acetylcholinesterase sits in the synapse between nerve cells and muscle cells. The small opening in the middle of each acetylcholinesterase subunit allows acetylcholine to pass through. Next, the serine amino acid bonds with the acetyl group of acetylcholine, breaking the molecule. Then, in a matter of microseconds, a water molecule breaks the new bond, releasing acetic acid and restoring the serine to its original form.
In current clinical practices, doctors have used drugs to partially block acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer’s patients to strengthen nerve signals.